Shared memory
Shared memory is memory that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple programs with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant copies. Shared memory is an efficient means of passing data between programs as shown in figure 1.
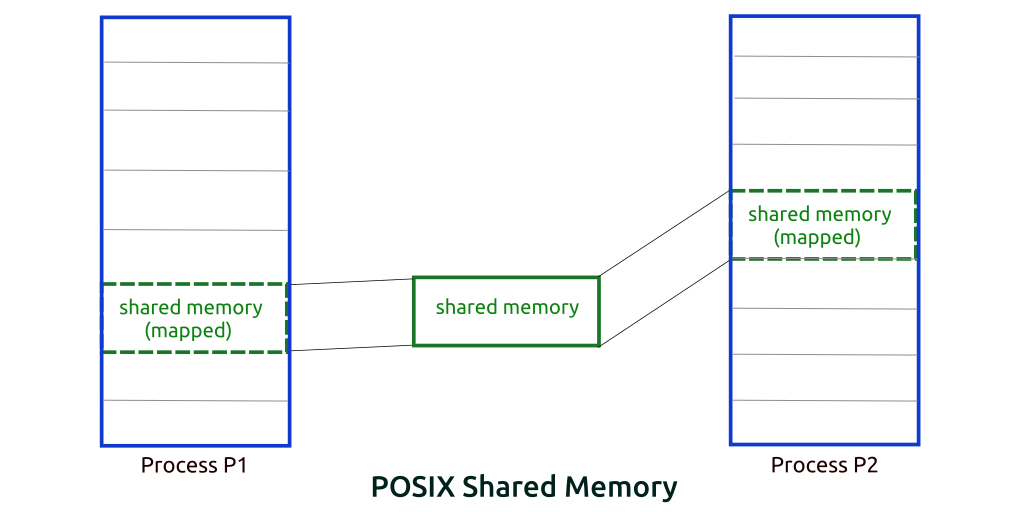 figure 1: how shared memory works
figure 1: how shared memory works
If a process want to access shared memory, it should: (use POSIX API)
1. Create, or gain access to, a shared memory object.
int shm_open (const char *name, int oflag, mode_t mode);
2. Map a shared memory object into its address space.
void *mmap (void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);
3. Do operations on shared memory (read, write, update).
4. Delete mappings of the shared memory object.
int munmap (void *addr, size_t length);
5. Destroy a shared memory object when no references to it remain open.
int shm_unlink (const char *name);