
to

to
Apache Giraph is an
open-source and distributed graph processing system based on
Google's Pregel.
It adopts vertex-centric programming model and is implemented by
re-using Hadoop MapReduce code base.
In this lab, we will teach you
Giraph jobs were consistently hanging if the hostname includes uppercase letters (which is a known bug). Say if you are using our VirtualBox image, you need to




Similar to developing MapReduce programs, we use Eclipse IDE to implement Giraph programs. Now, download our lab material giraph-lab.zip here and look at some examples.
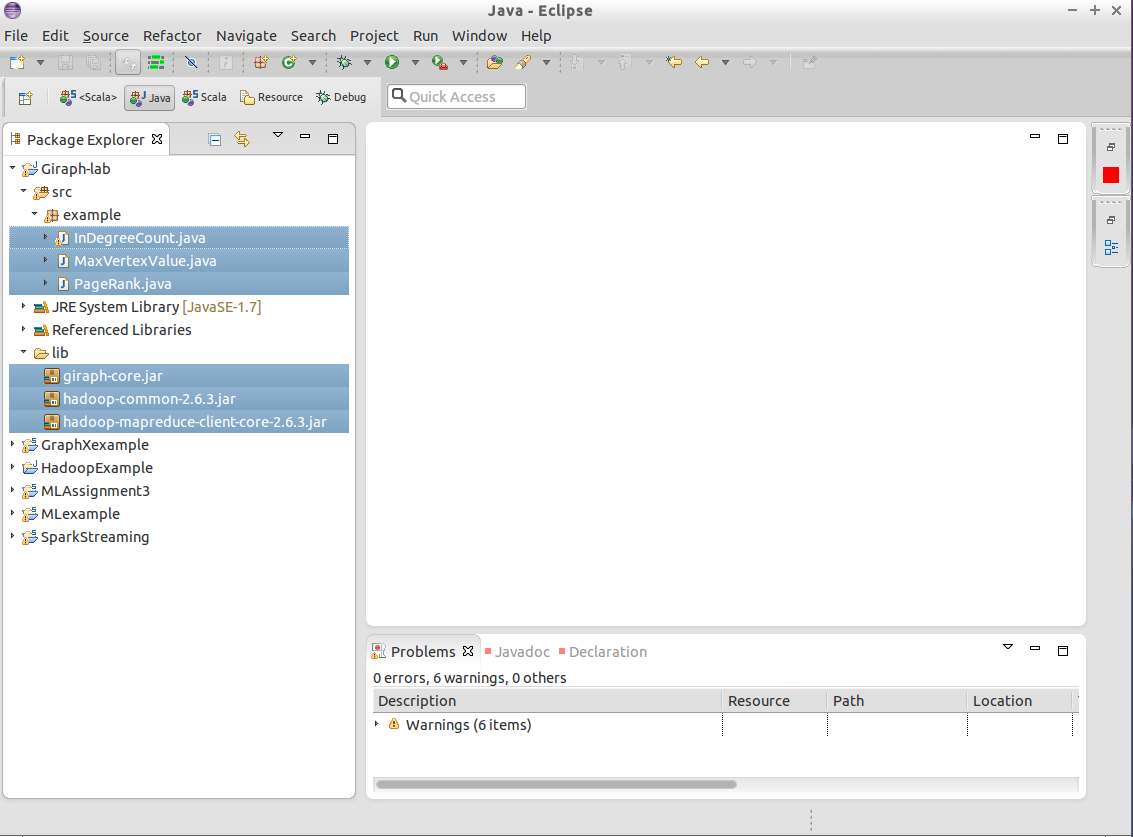
After importing the project, you will see 3 Java files in
src folder. Also, you will find giraph-core.jar, hadoop-common-2.6.3.jar and hadoop-mapreduce-client-core-2.6.3.jar
in lib folder. The first one is the Giraph core library while the
other two are Hadoop libraries (you met before in MapReduce Lab).
Let's have a quick look at MaxVertexValue.java. Its code is shown as below.
package example;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.giraph.graph.Vertex;
import org.apache.giraph.graph.BasicComputation;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.DoubleWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.FloatWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
/**
Vertex ID: LongWritable
Vertex value: DoubleWritable
Edge value: FloatWritable
Message: DoubleWritable
Assumption:
1. The graph is strongly connected
*/
public class MaxVertexValue extends BasicComputation<LongWritable, DoubleWritable, FloatWritable, DoubleWritable> {
@Override
public void compute(Vertex<LongWritable, DoubleWritable, FloatWritable> vertex,
Iterable<DoubleWritable> messages) throws IOException {
boolean changed = false;
for (DoubleWritable msg : messages) {
/* Collect messages from in-neighbours and update if necessary */
if ( vertex.getValue().get() < msg.get() ) {
vertex.setValue( new DoubleWritable( msg.get() ) );
changed = true;
}
}
/* Send the message to out-neighbours at Superstep 0 or Vertex value is changed */
if ( getSuperstep() == 0 || changed ) {
sendMessageToAllEdges(vertex, getValue());
}
vertex.voteToHalt();
}
}
To use Giraph's vertex-centric model, your class should extend org.apache.giraph.graph.BasicComputation<I,
V, E, M> and implement compute() method.
The meanings of <I, V, E, M> are as follows.
An important member function of BasicComputation class is getSuperstep(), which obtains the current step number. Note that it starts from zero.
As an argument of compute() method, vertex with type org.apache.giraph.graph.Vertex<I,V,E> has some useful functions:
PageRank algorithm is used by Google to rank search engine results. PageRank represents the importance of a web page. PageRank algorithm in vertex-centric implementation is as follows, assuming we are given the maximum number of supersteps MAX_STEPS.
package example;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.giraph.graph.Vertex;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.DoubleWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.FloatWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.giraph.graph.BasicComputation;
public class PageRank extends BasicComputation<LongWritable, DoubleWritable, FloatWritable, DoubleWritable> {
/* Maximum number of iterations */
public final static long MAX_STEPS = 30;
@Override
public void compute(Vertex<LongWritable, DoubleWritable, FloatWritable> vertex,
Iterable<DoubleWritable> messages) throws IOException {
if (getSuperstep() >= 1) {
double sum = 0;
/* Collect PageRank from in-neighbors */
for (DoubleWritable msg : messages) {
sum += msg.get();
}
/* Update PageRank */
DoubleWritable vertexValue =
new DoubleWritable((0.15d / getTotalNumVertices()) + 0.85d * sum);
vertex.setValue(vertexValue);
}
if (getSuperstep() < MAX_STEPS) {
/* Send updated PageRank to out-neighbors */
sendMessageToAllEdges(vertex,
new DoubleWritable(vertex.getValue().get() / vertex.getNumEdges()));
} else {
/* Stop */
vertex.voteToHalt();
}
}
}
The idea of PageRank:
Export your project to a JAR with the following settings.
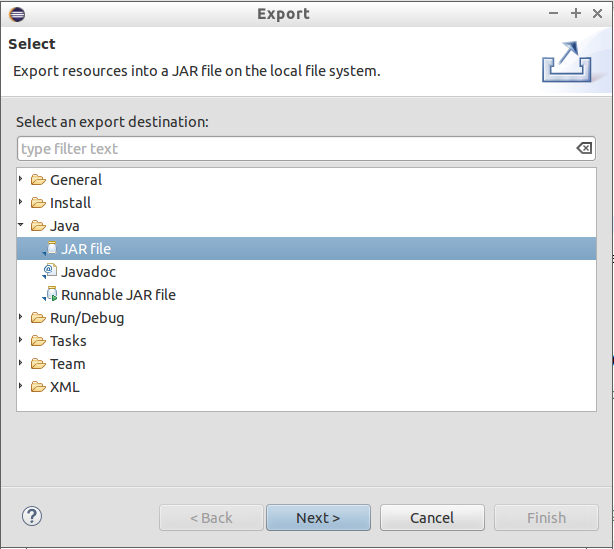
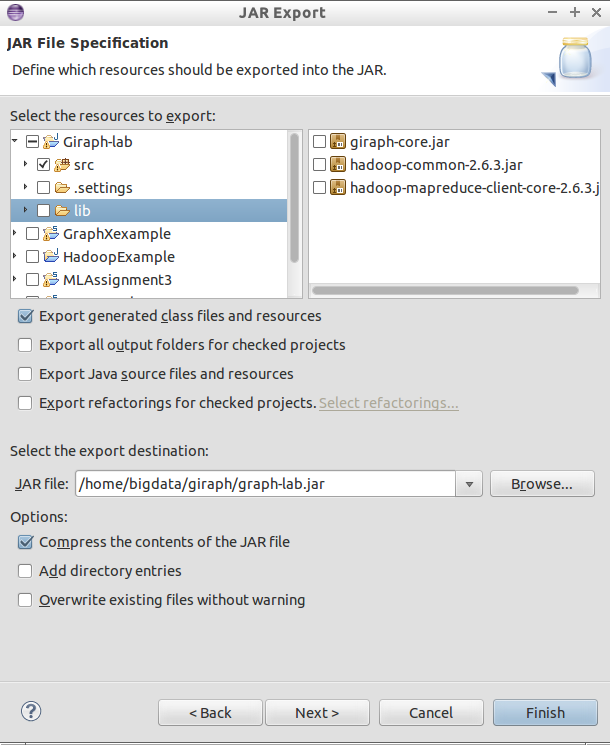
Please download two example graph data files graph-data1.txt and graph-data2.txt.
They have the following format: Each line below has the
adjacency-list format [source_id,source_value,[[dest_id,edge_weight],[dest_id,edge_weight],...]].
This format is called JsonLongDoubleFloatDoubleVertexInputFormat.
The content of graph-data1.txt is as follows:
[0,100,[[1,1],[3,3]]]
[1,20,[[0,1],[2,2],[3,1]]]
[2,90,[[1,2],[4,4]]]
[3,50,[[0,3],[1,1],[4,4]]]
[4,80,[[3,4],[2,4]]]
For example, [2,90,[[1,2],[4,4]]] means Node 2 has vertex
value of 90. It has an edge to Node 1 with weight 2 and has another
edge to Node 4 with weight 4.
Now, you start Hadoop, upload graph-data1.txt to HDFS and execute your Giraph programs.
# Start Hadoop
$ cd ~/Programs/hadoop/sbin
$ ./start-all.sh
$ cd ../bin
# Note: current directory is ~/Programs/hadoop/bin
# Create folder in HDFS if not exist
$ ./hadoop fs -mkdir -p /user/bigdata/giraph/input
# Upload graph-data1.txt to HDFS, assume it is at ~/
$ ./hadoop fs -put ~/graph-data1.txt /user/bigdata/giraph/input/graph-data1.txt
# Execute Giraph program
$ ./hadoop jar ../share/hadoop/common/giraph-core.jar org.apache.giraph.GiraphRunner example.MaxVertexValue -vif org.apache.giraph.io.formats.JsonLongDoubleFloatDoubleVertexInputFormat -vip /user/bigdata/giraph/input/graph-data1.txt -vof org.apache.giraph.io.formats.IdWithValueTextOutputFormat -op /user/bigdata/giraph/output -w 1 -ca giraph.SplitMasterWorker=false
# Display output file
$ ./hadoop fs -cat /user/bigdata/giraph/output/part-m-00000
Explanation:

Let's upload graph-data2.txt to HDFS and execute PageRank. The expected output is as follows.
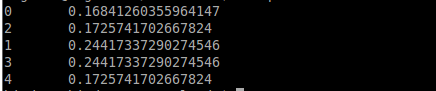
|
Code Snippet 1: sendMessage(edge.getTargetVertexId(), new DoubleWritable(1.0)); |
|
Code Snippet 2: sum++; |